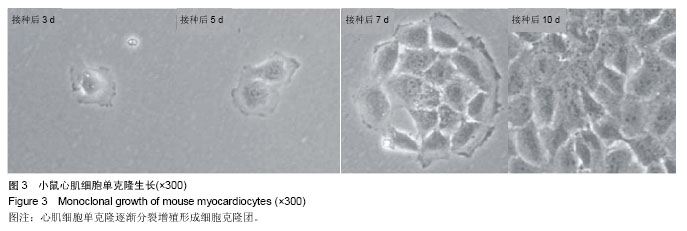
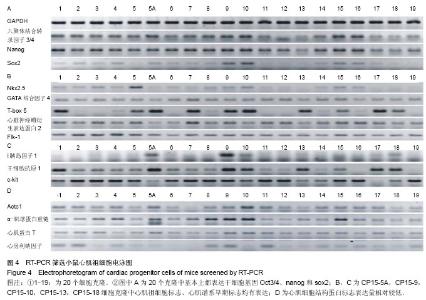
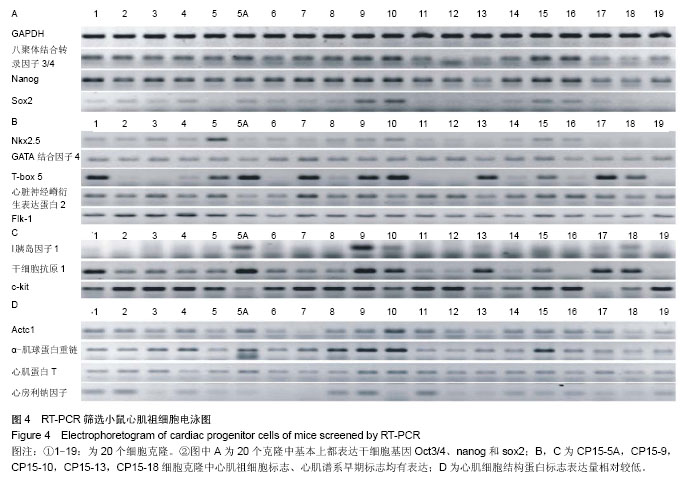
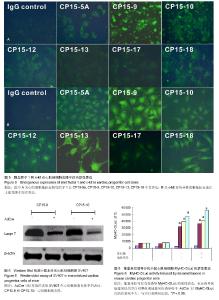
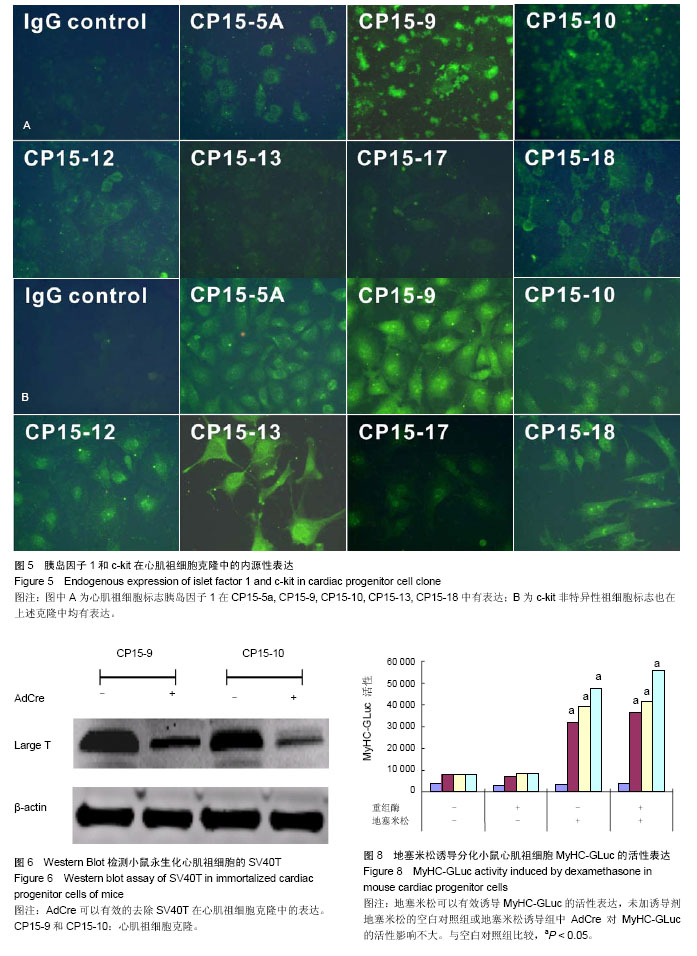
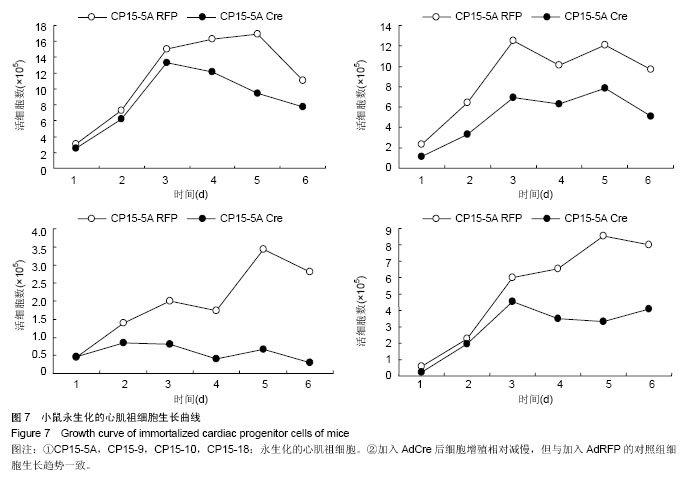
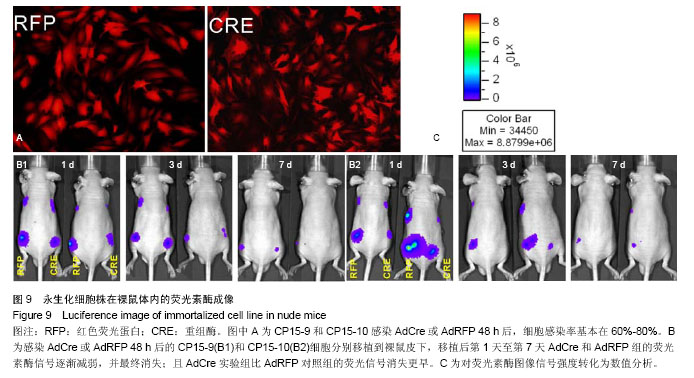
| [1] Doppler SA, Deutsch MA, Krane M, et al. Cardiac regeneration: current therapies- future concepts.J Thorac Dis.2013; 5(5):683-697.
[2] Nguyen PK, Riegler J, Wu JC. Stem Cell Imaging: From Bench to Bedside. Cell Stem Cell.2014; 3;14(4):431-444.
[3] Sharma A, Wu JC, Wu SM.Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes for cardiovascular disease modeling and drug screening. Stem Cell Res Ther.2013; 24; 4(6):150.
[4] Pfister O, Della Verde G, Kuster GM, et al.Regenerative therapy for cardiovascular disease. Transl Res.2014;163(4): 307-320.
[5] Matsa E, Sallam K, Wu JC. Cardiac stem cell biology: glimpse of the past, present, and future. Circ Res.2014; 3; 114(1): 21-27.
[6] Ye J, Yeghiazarians Y. Cardiac stem cell therapy: review of the native cardiac progenitor cells and future direction. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2014; 63(2): 85-94.
[7] Ba MC, Zhou XD, Liu L, et al.Proliferation of retrorsine-treated SD rat immortalized hepatocytes after intrasplenic transplantation. Di Yi Jun Yi Da Xue Xue Bao.2003; 23(6): 546-548, 552.
[8] Wang X, Cui J, He TC, et al. Decellularized liver scaffolds effectively support the proliferation and differentiation of mouse fetal hepatic progenitors. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014; 102(4): 1017-1025.
[9] Van Vliet P, Wu SM, Pucéat M, et al. Early cardiac development: a view from stem cells to embryos. Cardiovasc Res. 2012;96(3):352-362.
[10] Pandur P, Sirbu IO, Kühl M, et al.Islet1-expressing cardiac progenitor cells: a comparison across species.Dev Genes Evol.2013; 223(1-2):117-129.
[11] López-Sánchez C, García-Martínez V.Molecular determinants of cardiac specification. Cardiovasc Res.2011; 15; 91(2): 185-195.
[12] Sturzu AC, Wu SM.Developmental and regenerative biology of multipotent cardiovascular progenitor cells.Circ Res.2011; 4;108(3):353-364.
[13] Samal R, Ameling S, Hammer E, et al.OMICS-based exploration of the molecular phenotype of resident cardiac progenitor cells from adult murine heart. J Proteomics. 2012; 18; 75(17): 5304-5315.
[14] Tillmanns J, Rota M, Hosoda T, et al.Formation of large coronary arteries by cardiac progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2008;105(5):1668-1673.
[15] Takamiya M, Haider KH, Ashraf M. Identification and characterization of a novel multipotent sub-population of Sca-1+ cardiac progenitor cells for myocardial regeneration. PLoS One. 2011; 6(9):e25265.
[16] Nelson TJ, Chiriac A, Terzic A, et al.Lineage specification of Flk-1+ progenitors is associated with divergent Sox7 expression in cardiopoiesis. Differentiation.2009; 77(3): 248-255.
[17] Ale A, Siebenhaar F, Wildgruber M, et al. Cardioprotective c-kit(+) bone marrow cells attenuate apoptosis after acute myocardial infarction in mice - in-vivo assessment with fluorescence molecular imaging. Theranostics.2013;2; 3(11): 903-913.
[18] Laugwitz KL, Moretti A, Lam J, et al.Postnatal isl1+ cardioblasts enter fully differentiated cardiomyocyte lineages.Nature.2005;433(7026): 647-653.
[19] Moretti, A, Caron L, Nakano A, et al, Multipotent embryonic isl1+ progenitor cells lead to cardiac, smooth muscle, and endothelial cell diversification. Cell. 2006;127(6): 1151-1165.
[20] Di Felice V, Zummo G.Stem cell populations in the heart and the role of Isl1 positive cells. Eur J Histochem.2013;9; 57(2): e14.
[21] Hotchkiss A, Feridooni T, Pasumarthi KB, et al.The effects of calcium channel blockade on proliferation and differentiation of cardiac progenitor cells.Cell Calcium. 2014;55(5):238-251.
[22] Vanelli A, Pennarossa G, Brevini TA, et al.Isolation, characterization and differentiation potential of cardiac progenitor cells in adult pigs. Stem Cell Rev. 2012; 8(3): 706-719. |